Bookkeeping
What Is the Accounting Equation Formula?
The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. If the left side of the accounting equation (total assets) increases or decreases, the right side (liabilities and equity) also changes in the same direction to balance the equation. In above example, we have observed the impact of twelve different transactions on accounting equation. Notice that each transaction changes the dollar value of at least one of the basic elements of equation (i.e., assets, liabilities and owner’s equity) but the equation as a whole does not lose its balance.
Expanded Accounting Equation Formula
Long-term liabilities are usually owed to lending institutions and include notes payable and possibly unearned revenue. The inventory (asset) of the business will increase by the $2,500 cost of the inventory and a trade payable (liability) will be recorded to represent the amount now owed to the supplier. In the above transaction, Assets increased as a result of the increase in Cash. At the same time, Capital increased due to the owner’s contribution. Remember that capital is increased by contribution of owners and income, and is decreased by withdrawals and expenses.
Financial statements
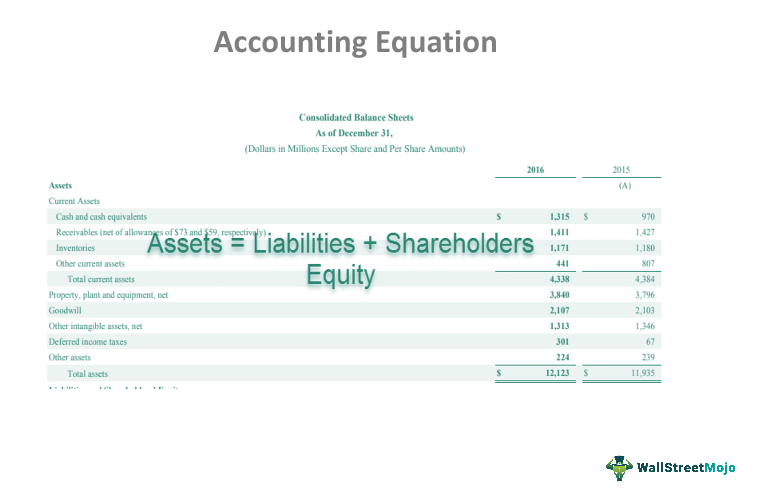
If a company’s stock is publicly traded, earnings per share must appear on the face of the income statement. The accounting equation is based on the premise that the sum of a company’s assets is equal to its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity. As a core concept in modern accounting, this provides the basis for keeping a company’s books balanced across a given accounting cycle. Equity on the other hand is the shareholders’ claims on the company assets. This is the amount of money shareholders have contributed to the company for an ownership stake.
Components of the Basic Accounting Equation
On 28 January, merchandise costing $5,500 are destroyed by fire. The effect of this transaction on the accounting equation is the same as that of loss by fire that occurred on January 20. This transaction also generates a profit of $1,000 for Sam Enterprises, which would increase the owner’s equity element of the equation. On 2 January, Mr. Sam purchases a building for $50,000 for use in the business.
- This business transaction increases company cash and increases equity by the same amount.
- The combined balance of liabilities and capital is also at $50,000.
- In this case, Speakers, Inc. uses its cash to buy another asset, so the asset account is decreased from the disbursement of cash and increased by the addition of installation equipment.
- $10,000 of cash (asset) will be received from the bank but the business must also record an equal amount representing the fact that the loan (liability) will eventually need to be repaid.
Our PRO users get lifetime access to our accounting equation visual tutorial, cheat sheet, flashcards, quick test, and more. This is how the accounting equation of Laura’s business looks like after incorporating the effects of all transactions at the end of month 1. In this example, we will see how this accounting equation will transform once we consider the effects of transactions from the first month of Laura’s business.
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question

One of the main financial statements (along with the balance sheet, the statement of cash flows, and the statement of stockholders’ equity). The income statement is also referred to as the profit and loss statement, P&L, statement of income, and the statement of operations. The income statement reports the revenues, gains, expenses, losses, net income and other totals for the period of time shown in the heading of the statement.
The difference of $500 in the cash discount would be added to the owner’s equity. On 12 January, Sam Enterprises pays $10,000 cash to its accounts payable. This transaction would reduce an asset (cash) and a liability (accounts payable). The Accounting Equation is a vital formula to understand and consider when it comes to the financial health of your business.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the equation, let’s take a look at each accounting equation component starting with the assets. Shareholders’ equity is the total value of the company expressed in dollars. Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them. The accounting equation matters because keeping track of each transaction’s corresponding entry on each side is essential for keeping records accurate.
Equity is usually shown after liabilities in the accounting equation because liabilities must have to be repaid before owners’ claims. You might also notice that the accounting equation is in the same order as the balance sheet. The owner’s equity is the balancing amount in the accounting equation. So whatever difference between cloud engineer and devops engineer the worth of assets and liabilities of a business are, the owners’ equity will always be the remaining amount (total assets MINUS total liabilities) that keeps the accounting equation in balance. All assets owned by a business are acquired with the funds supplied either by creditors or by owner(s).
Creditors have preferential rights over the assets of the business, and so it is appropriate to place liabilities before the capital or owner’s equity in the equation. Once all of the claims by outside companies and claims by shareholders are added up, they will always equal the total company assets. The business has paid $250 cash (asset) to repay some of the loan (liability) resulting in both the cash and loan liability reducing by $250. Required Explain how each of the above transactions impact the accounting equation and illustrate the cumulative effect that they have.

